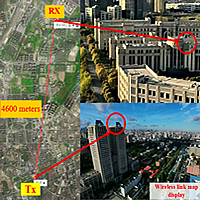
Over 100 Gb/s mm-wave delivery with 4600 m wireless distance based on dual polarization multiplexing
Li W P, Yu J J, Ji X X, et al
Sci China Inf Sci, 2023, 66(12): 224301
With the rapid development of network services and the emergence of emerging technologies such as big data, Internet of vehicles, and 5G communications, the traffic of digital mobile devices and various network services has increased dramatically, which puts forward higher requirements on the transmission capacity and wireless distance of data communication. Radio over fiber (ROF) technology is an emerging wireless broadband access technology that integrates the advantages of fiber optic communication with large bandwidth and anti-electromagnetic interference, as well as the advantages of wireless mobile communication with low cost and good mobility. As shown in Figure 1(a), the basic architecture of an ROF system usually consists of central stations and base stations. In the central station, the data is modulated onto the optical carrier through an electro-optical modulator (Mod), and the modulated signals are subjected to a series of changes and processing in the optical domain. Then the processed optical signals are transmitted to the base station employing fiber optic remote technology. In the base station, a photodiode (PD) is used to convert the optical signals into electrical signals, and the antennas are used to propagate the radio wave signals.